
Use the DePriester chart: a. 4.PTT 201/4THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (2013/2014) Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium (VLE) Solution Thermodynamic:Transcribed image text: A8. Preferred analytical correlations are less empirical in nature and most often are theoretically based on one of two exact thermodynamic formulations, as derived in Sec. (a) Low-temperature range. 13-14 K values (K y/x) in light-hydrocarbon systems.
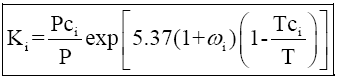
As pressure reduces, more & more L vaporizes until completed at W point where last drop of L (dew) disappear – dew point: a point when a vapor forms the first droplet of liquid and begins to condense Fig. Liquid at F, reduces pressure at constant T & composition along FG, the first bubble appear at L – bubble point: a point when a liquid forms the first bubble of vapor and begins to evaporate contact to each other in a closed location takes place when liquid and vapor are allowed to
Isomers such as ortho-, meta- & para-xylene) Assumptions Dewpoint & Bubblepoint Calculations with Raoult’s Law FIND GIVEN BUBL P: Calculate and PFor binary systems to solve for bubblepoint calculation (T is given) 2 3Raoult’s law equation can be solved for xi to solve for dewpoint calculation (T is given) 4 5Example 1 Binary system acetonitrile(1)/nitromethane(2) conforms closely to Raoult’s law. Valid only if the species are chemically similar (size, same chemical nature e.g. Applicable for low to moderate pressure
At 750C, the saturated pressure is given by Antoine equation Substitute both values in (A) to find P The corresponding value of y1 is found from Eq. Since this is a binary system, Eq. Y1 for a pressure of 70 kPaA) BUBL P calculations are required. Prepare a graph showing t vs. Prepare a graph showing P vs.
1, This is the liquid-phase composition at point c’ b) When P is fixed, the T varies along T1sat and T2sat, with x1 & y1. 3 For y1=0.6 and t=750CAnd by Eq. Thus DEW P calculations are required.
For pressure low It is so low that it can be assume as ideal gas For example Get y1 from Eq. Substituting T= 78˚C into (i) and (ii) P1sat = 91.76 kPa P2sat = 46.84 kPa e.g select T= 78˚C Evaluate x1 by Eq. Select T between these two temperatures and calculate P1sat & P2sat for the two temperatures.
Thus, activity coefficient is introduced in Raoult’s Law 7Activity coefficients are function of T & liquid phase composition, x Since For bubble point 8 For dew point 9 1 written for species 2 Whence y1=1-y2=0.9988, and the vapor phase is nearly pure CO2, as expected.VLE BY MODIFIED RAOULT’S LAW The 2nd assumption of Raoult’s Law is abandoned, taking into account the deviation from solution ideality in L phase. Henry’s constant for CO2 in water at 100C is about 990 bar and x1=0.01.Henry’s law for species 1 & Raoult’s law for species 2 are written With H1=990 bar & P2sat = 0.01227 bar (from steam tables at 100C)Then by Raoult’s law, Eq.
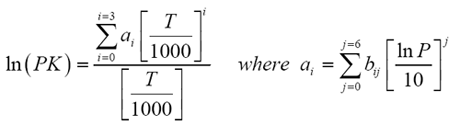


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
